Optimizing Composting: Exploring Effective Aeration Techniques
Composting requires proper aeration for effective organic waste transformation into nutrient-rich so…….

Composting requires proper aeration for effective organic waste transformation into nutrient-rich soil amendments. Techniques like turning piles or using specialized equipment ensure optimal conditions, speeding up decomposition and preventing stagnation. Different methods, from manual to advanced mechanical systems, cater to various scales and requirements. Passive approaches take longer but produce high-quality compost, while active techniques offer precise control for rapid decomposition in larger operations. Future innovations in aeration technology aim to make composting more efficient and sustainable through smart sensors, automation, and renewable energy sources.
Compost aeration is a vital aspect of effective composting, ensuring optimal decomposition and nutrient-rich end products. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of compost aeration techniques, exploring why it matters and how various methods influence the composting process. From understanding the fundamentals to considering advantages, disadvantages, and future trends, this article equips readers with insights to optimize their composting journey. Discover the best practices for successful compost management.
- Understanding Compost Aeration: Why It Matters
- Common Methods of Compost Aeration
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Techniques
- Choosing the Right Aeration System for Your Composting Needs
- Best Practices for Effective Compost Aeration
- Future Trends in Compost Aeration Technology
Understanding Compost Aeration: Why It Matters

Composting is a natural process that transforms organic waste into nutrient-rich soil amendment, but proper aeration is crucial for its effectiveness and efficiency. Understanding compost aeration involves grasping why oxygen plays a vital role in the decomposition of organic materials. Just like living organisms need oxygen to thrive, microorganisms responsible for composting require it to break down waste materials.
Adequate aeration ensures efficient decomposition, reduces bad odors, prevents pile compression, and promotes faster composting. Without proper air circulation, compost piles can become stagnant, leading to slow breakdown, undesirable conditions for beneficial microbes, and potential health hazards due to emitted gases. By incorporating aeration techniques such as turning the pile or using specialized equipment, composters can maintain optimal conditions for productive and healthy decomposition.
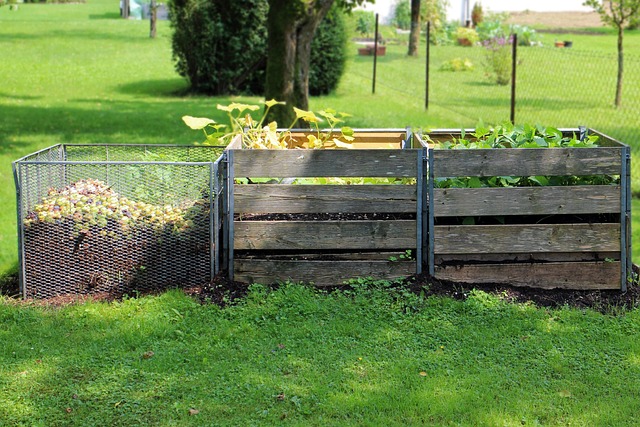
Common Methods of Compost Aeration

Compost aeration is a vital process in effective and efficient composting, ensuring optimal conditions for decomposition. There are several common methods employed to introduce air into compost piles, each with its unique advantages. One traditional technique involves turning the pile by hand or using machinery, allowing oxygen to reach all parts of the material. This physical manipulation not only aerates the compost but also helps mix different components, promoting a more even breakdown of organic matter.
Another popular method is the use of aeration systems that blow or inject air directly into the compost stack. These systems are particularly beneficial for larger-scale composting operations, such as those in commercial facilities or municipal waste management centers. By efficiently distributing oxygen throughout the pile, these techniques accelerate the decomposition process, reducing the time required to transform organic waste into nutrient-rich compost.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Techniques

Different compost aeration techniques offer varying advantages and disadvantages, each with its own impact on the composting process and final product. Active methods like stirring and turning involve manual or mechanical intervention to introduce oxygen into the pile. These promote faster decomposition by preventing a lack of airflow, resulting in nutrient-rich compost in a shorter time frame. However, they demand more effort and can be labor-intensive, especially for larger-scale operations.
Passive techniques, such as creating layers or using compost tumblers, require less human intervention but may take longer to produce finished compost. They are ideal for those seeking low-maintenance solutions and result in high-quality compost with a fine texture. Yet, their efficiency is generally lower compared to active methods, making them more suitable for smaller-scale composting needs.
Choosing the Right Aeration System for Your Composting Needs

When selecting an aeration system, consider your specific composting needs and scale. For smaller-scale composters, passive aeration methods like tumblers or bin designs with well-ventilated walls can be efficient. These simple yet effective systems allow oxygen to enter naturally, supporting microbial activity without requiring external machinery.
For larger operations or those aiming for faster decomposition, active aeration techniques are worth exploring. These involve blowing air into the compost pile, either through ventilation pipes or mechanical agitators. Active systems offer greater control over temperature and aeration levels, accelerating the composting process while producing high-quality compost suitable for various applications.
Best Practices for Effective Compost Aeration

Maintaining proper aeration is key to successful and efficient composting. One of the best practices involves incorporating mechanical aerators, such as compost turners or aerating drills, especially in larger-scale composting operations. These machines gently mix and turn the compost pile, ensuring optimal oxygen levels throughout. Regular turning also helps prevent the buildup of moist, dense layers on the pile’s surface, which can hinder decomposition.
Additionally, for smaller-scale composting at home, it’s beneficial to ensure a balance between adding green (nitrogen-rich) and brown (carbon-rich) materials. This equilibrium supports a thriving microbial community, enhancing the aeration process naturally. Turning the compost pile every few days further facilitates air circulation and speeds up the transformation of organic waste into nutrient-rich compost.
Future Trends in Compost Aeration Technology

The future of compost aeration technology looks promising, with innovations aimed at enhancing efficiency and sustainability in the composting process. One emerging trend is the integration of smart sensors and automation to monitor and control oxygen levels, temperature, and moisture content in compost piles. These advanced systems can optimize turning and mixing frequencies, ensuring ideal conditions for efficient decomposition.
Additionally, renewable energy sources are expected to play a significant role in powering aeration systems. Solar panels and wind turbines integrated into composting facilities can reduce operational costs and environmental impact. As the demand for eco-friendly practices continues to rise, these future trends in compost aeration technology will contribute to a more sustainable approach to organic waste management, ultimately promoting circular economy principles through enhanced composting processes.