Navigating Composting Laws: A U.S. and Global Guide to Regulations and Sustainable Practices
National legislation across different countries, including the U.S., has established comprehensive r…….

National legislation across different countries, including the U.S., has established comprehensive regulations on composting to promote sustainable waste management. These laws set industry standards for organic waste acceptance and processing, ensuring the production of high-quality compost suitable for agricultural and horticultural use. They also mandate educational programs to raise public awareness and encourage compliance with local regulations, which in turn helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions from landfills. In the U.S., states like California have enacted stringent measures to manage organic waste, while New York has expanded composting programs to include food scraps. Massachusetts and Connecticut support these efforts with incentives and educational initiatives. Globally, the European Union's Organic Waste Recycling Regulation reflects its commitment to sustainable resource management, and the FAO advocates for composting as a key practice in waste management systems, highlighting its role in soil health, greenhouse gas reduction, and aligning with circular economy principles. Innovations such as aerated static pile systems, thermophilic composting, in-vessel composting technologies, and biofilters are transforming the industry by improving operational efficiency and minimizing environmental impact. The integration of smart technology further enhances these processes, underscoring composting's importance in sustainable waste management globally.
Composting has emerged as a cornerstone in sustainable waste management, offering a natural solution to organic waste disposal while enriching soil health. This article delves into the intricacies of composting laws and regulations that govern this eco-friendly practice. We explore national frameworks that set the tone for composting practices, highlight state-specific regulations across the USA, and cast a global gaze at international perspectives on composting laws and guidelines. Furthermore, we uncover best practices and innovative approaches in composting that pave the way towards more sustainable waste management systems. Join us as we navigate the legal landscape of composting, ensuring a greener future for our planet.
- National Frameworks Governing Composting Practices: An Overview
- State-Specific Regulations and Composting Requirements Across the USA
- International Perspectives on Composting Laws and Guidelines
- Best Practices and Innovations in Composting for Sustainable Waste Management
National Frameworks Governing Composting Practices: An Overview
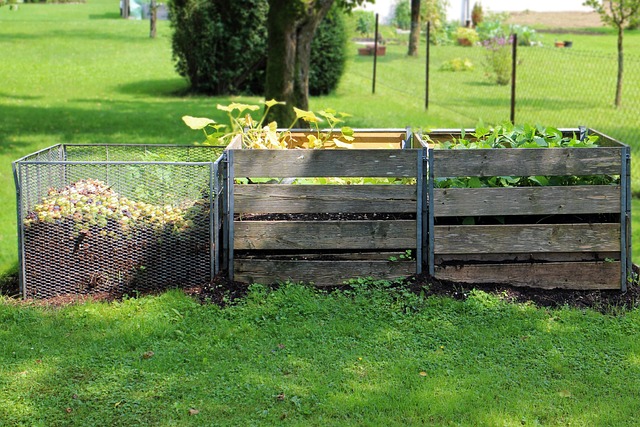

Composting practices are increasingly gaining attention due to their significance in waste management and sustainability efforts. Across various nations, legislative frameworks have been established to regulate composting activities. These national frameworks outline the standards and practices for both organic waste collection and compost utilization, ensuring environmental protection and the promotion of circular economy principles. The guidelines typically cover the acceptance criteria for source-separated organics, composting methods, quality standards for finished compost, and the application of compost in agriculture and horticulture. Additionally, these frameworks often include provisions for education and outreach to encourage community participation and compliance with local regulations. By setting clear objectives and responsibilities, such national laws and guidelines facilitate the transition towards more sustainable waste management practices and contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions associated with landfills.
Furthermore, these national frameworks are dynamic, adapting to advancements in composting technology and the evolving needs of society. They ensure that composting initiatives align with broader environmental goals and integrate with other waste management systems. Compliance with these regulations not only promotes the proper decomposition of organic matter but also supports the production of a valuable product that can enhance soil health and biodiversity. The frameworks also encourage innovation in the composting industry, fostering research and development to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of composting processes. As a result, the role of national regulations is pivotal in standardizing composting practices and ensuring their environmental, economic, and social benefits are maximized.
State-Specific Regulations and Composting Requirements Across the USA

In the realm of sustainable waste management, composting has emerged as a cornerstone practice across the United States. Each state within the nation has developed its own set of regulations and requirements to govern composting practices, reflecting both regional diversity in organic waste sources and local environmental priorities. For instance, California’s composting laws are stringent, focusing on reducing methane emissions by mandating aerobic composting for organic waste from both residential and commercial entities. The state also encourages the use of compost in agricultural settings to improve soil health. In contrast, states like New York have implemented comprehensive organics recycling programs that not only cover the traditional yard trimmings but also include food scraps through a network of community composting facilities. These initiatives aim to divert significant volumes of organic waste from landfills, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting a more sustainable environment.
Furthermore, states such as Massachusetts and Connecticut have established statewide composting goals and infrastructure support to facilitate the growth of local composting operations. The regulations vary from providing tax incentives for businesses that invest in composting facilities to setting up educational programs that inform citizens about the benefits of composting and how to participate effectively. These efforts underscore a commitment to not only manage waste responsibly but also to foster a community-driven approach to environmental stewardship. Across the nation, states are continually updating their composting requirements to align with evolving sustainability goals and to address emerging challenges in waste management. This patchwork of state-specific regulations reflects the dynamic nature of composting as an integral component of America’s waste reduction strategy.
International Perspectives on Composting Laws and Guidelines

Composting laws and regulations vary significantly across different countries, reflecting both regional biodiversity and cultural attitudes towards waste management. In Europe, for instance, the European Union’s Regulation on Organic Waste Recycling sets mandatory targets for member states to divert organic waste from landfills by converting it into compost. This initiative is a testament to the EU’s commitment to sustainable resource management and contributes to its broader environmental goals. The United States, while not as stringently regulated at the federal level, has individual states with varied composting laws. California, for example, has some of the most progressive regulations aimed at reducing organic waste in landfills through composting programs. These state-specific guidelines often incentivize community and commercial participation, thereby encouraging a more sustainable approach to managing organic waste.
At an international level, the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations promotes the adoption of composting as part of a holistic waste management strategy through its guidelines and recommendations. These guidelines emphasize the importance of composting in maintaining soil health, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and contributing to circular economy principles. Additionally, international frameworks like the Paris Agreement recognize composting as a key practice in mitigating climate change by diverting methane-producing waste from landfills. As such, there is a growing consensus among nations on the necessity of implementing effective composting laws and regulations to support sustainable development goals. This global perspective underscores the critical role that composting plays in environmental stewardship and waste management strategies worldwide.
Best Practices and Innovations in Composting for Sustainable Waste Management

Composting plays a pivotal role in sustainable waste management, offering an eco-friendly solution to organic waste disposal. Best practices in composting emphasize the importance of balancing green and brown organic materials to create optimal conditions for microbial activity. This balance ensures efficient decomposition, resulting in nutrient-rich compost that can enhance soil health and fertility. Innovations in this field include the development of aerated static pile (ASP) systems, which facilitate better airflow and moisture management within composting piles. These systems are particularly beneficial for large-scale operations as they reduce labor costs and increase the efficiency of the composting process. Additionally, the integration of thermophilic composting techniques leverages high temperatures to kill pathogens and weed seeds more effectively than traditional methods.
Furthermore, the adoption of in-vessel composting technologies offers a controlled environment that minimizes odors and pests, making it suitable for urban settings. These systems utilize advanced mixing and aeration mechanisms to ensure uniform decomposition. In terms of innovation, the use of composting biofilters for treating organic waste is gaining traction. Biofilters contain microorganisms that break down contaminants in a controlled setting, which not only reduces methane emissions but also generates valuable compost. The integration of these technologies with smart sensors and monitoring systems enables real-time data collection for process optimization, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency of composting operations. As communities and regions continue to refine their composting practices, the potential for sustainable waste management grows, offering a promising path forward in the global effort to minimize environmental impact.